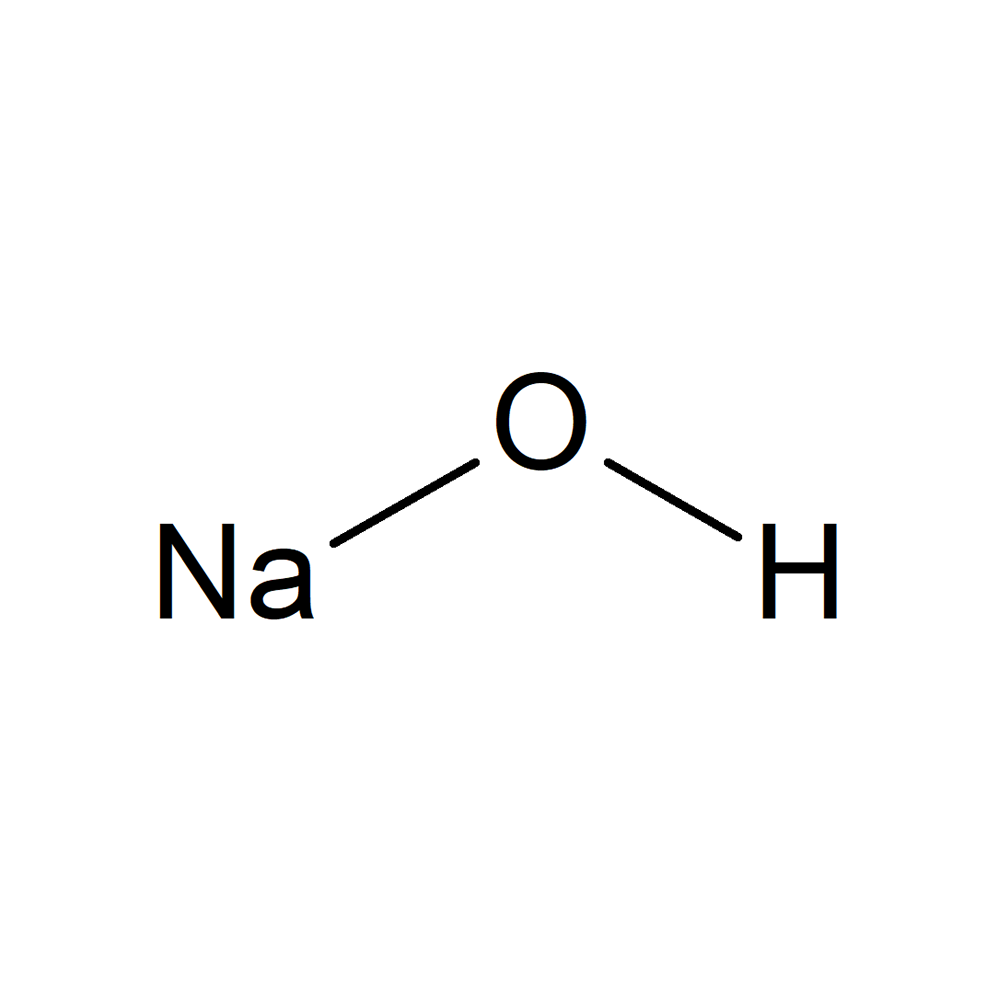
Sodium hydroxide, also known as caustic soda or lye, is a white, odorless, corrosive, and highly alkaline solid or liquid chemical reagent that is used in many industrial and household applications: It is used as a neutralization agent, in petroleum refining, paper making, and in cleaning compounds and drain cleaners. It is a strongly corrosive, inorganic, water-soluble compound that reacts rapidly with water, moisture, and strong acids to release heat. It also reacts with metals like aluminum, lead, tin, or zinc to form hydrogen gas, which is flammable and explosive.
Applications
- Chemical reactions: Used as a reagent in the gold-catalyzed selective oxidation of glycerol to glyceric acid, as a catalyst for the cross-dehydrogenative coupling of alcohols and hydrosilanes, and as a base in the Sonogashira-type coupling of aryl halides and alkynes
- Titration
- Dissolution testing
- Impinger to remove acidic gases
- Cure some foods
- Soaps, detergents, and drain cleaners
- Paper production
- Explosives
- Petroleum products
- and much more
Appearance: White solid at room temperature, colorless liquid when dissolved in water
Properties: Reacts violently with water and strong acids, absorbs moisture from the air, and can generate enough heat to cause a fire
Safety: Toxic if ingested, can severely irritate skin, eyes, and mucous membranes
Some other uses of sodium hydroxide:
- Soapmaking: Sodium hydroxide reacts with fats and oils to produce soap and glycerin.
- Papermaking: Sodium hydroxide breaks down wood into pulp.
- Water treatment: Sodium hydroxide controls water acidity and removes heavy metals.
- Fuel cells: Sodium hydroxide is used in the production of fuel cells, which can produce electricity for transportation, materials handling,
- Food additive: The FDA allows sodium hydroxide as a food additive at levels lower than 1 percent.